What is Tesofensine? | Mechanism of Action & Benefits
Tesofensine peptide is a compound scientifically studied for its potential applications in managing obesity and appetite control. By targeting neurotransmitters in the brain, this innovative agent offers insights into weight management strategies in clinical research. Below is a detailed exploration of its mechanism, potential effects, and scientific findings.
What is Tesofensine?
Tesofensine functions as a presynaptic reuptake inhibitor for three key monoamine neurotransmitters—noradrenaline, dopamine, and serotonin. These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in regulating energy balance, mood, and appetite. Tesofensine was initially researched for treatment applications in neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
However, its development shifted focus when it was observed that patients on tesofensine experienced significant weight loss.
Mechanism of Action
Tesofensine primarily works by increasing the availability of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the brain. This enhanced activity of neurotransmitters impacts appetite regulation, energy metabolism, and overall body composition.
Unlike typical selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) used to address depression and eating disorders, tesofensine's broader effect on multiple neurotransmitter systems yields a more substantial impact on weight and appetite control.
Potential Benefits of Tesofensine in Research
Scientific studies have highlighted several promising benefits associated with tesofensine, including:
- Appetite suppression: Reducing the sensation of hunger to aid in lower calorie intake.
- Enhanced energy metabolism: Improving the body's efficiency to burn calories.
- Weight management: Achieving significant weight loss through dual appetite control and metabolic stimulation.
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Aiding in glucose regulation and reducing the risks associated with insulin resistance.
- Mood enhancement: Demonstrating potential anti-depressant effects linked to serotonin and dopamine activity.
- Neuroprotection: Offering secondary benefits such as potential protective effects on brain health.
Research-Backed Outcomes
One clinical trial examined tesofensine's impact on obese patients over a 24-week period. Participants who combined tesofensine intake with a calorie-restricted diet achieved more pronounced weight loss compared to those following diet and placebo alone.
Weight reductions ranged between 4.5% and over 10%, correlating to approximately 20 to 25 pounds of weight loss in certain cohorts.
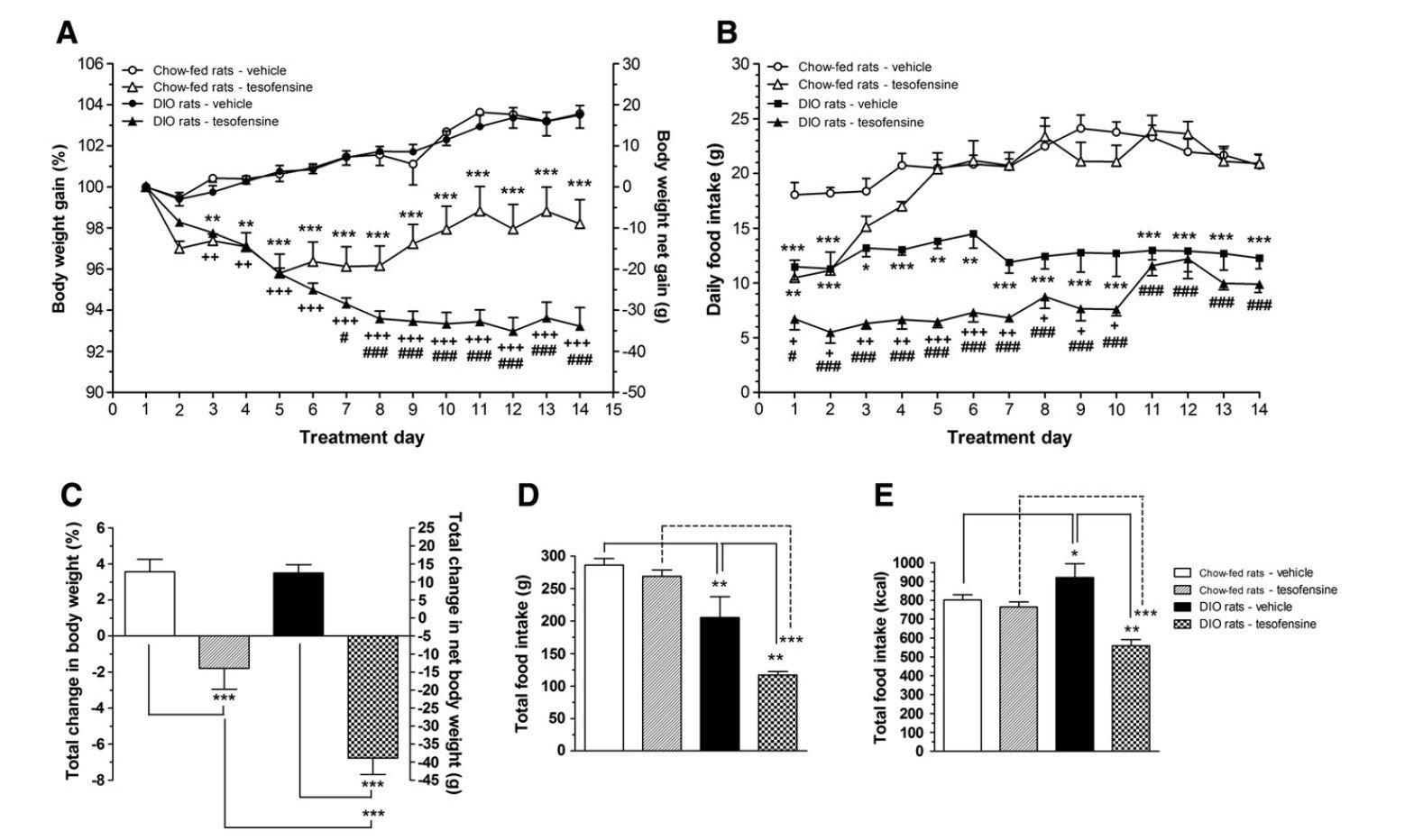
Experimental Findings in Animal Studies
Preclinical studies involving diet-induced obese (DIO) animal models provided similar findings, showcasing marked reductions in both body weight and appetite.
Tesofensine normalized forebrain dopamine levels, which are often diminished in subjects prone to obesity, further demonstrating its role in regulating dopaminergic activity.
Addressing Appetite Sensations and Satiety
One notable focus of tesofensine research is its ability to impact appetite sensations. Appetite, separate from physiological hunger, is influenced by hormonal and neural cues, particularly in individuals undergoing weight reduction. Tesofensine helps increase feelings of fullness (satiety) while reducing the drive for future food consumption.
Studies have demonstrated significant improvements in composite satiety scores (CSS)—a metric comprising satiety, fullness, and reductions in hunger signals—during tesofensine usage.
Dual Mechanism of Action
Research suggests tesofensine's weight-loss effects stem from two primary mechanisms:
- Appetite suppression: Positively influencing neurotransmitters involved in generating hunger and cravings.
- Thermogenesis stimulation: Potentially increasing fat oxidation and energy expenditure, particularly during night-time metabolic activity.
Applications in Obesity Management
Obesity poses a global health challenge as it increases the risk of comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers. While bariatric surgery remains a potent solution, pharmacological advancements, such as those offered by tesofensine, provide non-invasive alternatives.
Tesofensine may exhibit efficacy levels double that of current anti-obesity medications, signifying its potential utility in future medical protocols.
Considerations and Emerging Questions
Despite its promising results, the clinical use of tesofensine raises several scientific inquiries yet to be answered:
- Duration of Effectiveness: Some studies observed diminished appetite suppression effects after extended therapy, posing questions on tolerance.
- Safety Profile: Further studies are necessary to evaluate long-term safety and potential side effects.
- Targeted Applications: Continued exploration is needed to determine optimal dosage and patient profiles that may benefit most from tesofensine therapy.
A Cautious Outlook
While significant strides have been made in uncovering tesofensine's potential, it is important to emphasize that current studies are primarily conducted for research purposes.
The compound is not approved for widespread therapeutic use and remains a subject of ongoing investigation by clinical and pharmacological researchers.
Summary of Key Findings:
- Mechanism: Tesofensine targets obesity by inhibiting neurotransmitter reuptake, increasing satiety, and elevating energy metabolism.
References:
- Gilbert, Jo-Anne, et al. "The Effect of Tesofensine on Appetite Sensations." Obesity, vol. 20, no. 3, 2012, pp. 553–561., https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2011.197.
- Astrup, Arne, et al. "Effect of Tesofensine on Bodyweight Loss, Body Composition, and Quality of Life in Obese Patients: A Randomised, Double
- Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial." The Lancet, vol. 372, no. 9653, 2008, pp. 1906–1913., https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(08)61525-1.
- Hansen, Henrik H., et al. "Tesofensine Induces Appetite Suppression and Weight Loss with Reversal of Low Forebrain Dopamine Levels in the Diet-Induced Obese Rat." Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, vol. 110, 2013, pp. 265–271., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2013.07.018.
PandaRoids Reviews
Please leave your review on products or service below.
For discounts, please contact us


